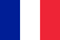
Varicose veins is a subcutaneous vein disease, which is expressed in excessive expansion and stretching, the elasticity of the veins is lost, the blood circulation process is disturbed. Varicose veins usually appear in the legs.
Varicose veins are considered a cosmetic problem, but if left untreated, they can cause complications. The main ones are trophic ulcers and thrombophlebitis, which develop in 70% of patients with varicose veins.
Symptoms of varicose veins
Signs that express themselves already in the early stages:
- legs get tired quickly;
- burning and heaviness in legs;
- small swelling appears;
- there is pain in the veins;
- there are cramps in the calf.
Another characteristic sign of varicose veins is the localization of pain in the calf, which appears in the evening and disappears in the morning. The pain is not sharp, the sensation is moderate, interesting.
In the first stage, dilated veins cannot be seen, but varicose veins have already developed. Sometimes it takes decades. Gradually, the symptoms become more disturbing, signs of venous insufficiency appear:
- leg swelling - in patients (most often it is women with varicose veins), chronic vein disease is usually accompanied by an increase in the volume of the lower leg. At the same time, edema, as well as pain and heaviness, are observed in the afternoon and subside after sleep. Leg edema is not typical for the mentioned pathology, it is a symptom of lymphatic edema;
- skin itching;
- knots, tortuosity, which can be seen with the naked eye;
- darkening, thickening of the skin, bluish appearance.
With the development of venous disease, the symptoms increase. There is a deterioration in the appearance of the skin of the legs, eczema and trophic ulcers appear.

Causes of varicose veins
The cause of varicose veins is a lack of leg vein valves, which causes the outflow of blood to deteriorate. The venous network in the leg consists of superficial and deep veins connected by vessels. Superficial veins carry blood away from the skin and subcutaneous structures, while deep veins carry it away from internal organs. The veins that connect them act as compensators that equalize the pressure in the superficial and deep vessels.
Proper blood flow goes in the direction from the superficial to the deep veins. This direction can be provided by the movement of the surrounding muscles and the work of the vasomotor center, since the movement from the bottom up is opposed to the traction force.
If for some reason the outflow becomes difficult, the walls of the vessels become inflamed, thinner, the veins dilate and cyanotic nodes characteristic of varicose veins appear.
The disease develops in response to a complex of unfavorable conditions mentioned below:
- hereditary - the weakness of the blood vessel walls can be transmitted from generation to generation and cause a loss of vascular tone;
- tiring work, standing on their feet - high-risk groups include people who, according to the nature of their activity, have to sit or stand for a long time;
- frequent pregnancy and childbirth - during this period, the amount of blood and pumping of the veins increases, which gives rise to varicose veins;
- obesity - increased venous pressure in overweight people increases the chance of varicose veins;
- failure in the hormonal system - self-administration of contraceptives and other drugs based on hormones causes changes in the vein walls. In women, such reactions can be observed during pregnancy;
- nutrition - the lack of fresh fruits and vegetables in the menu leads to a lack of fiber, as a result - weakening of the vein walls.
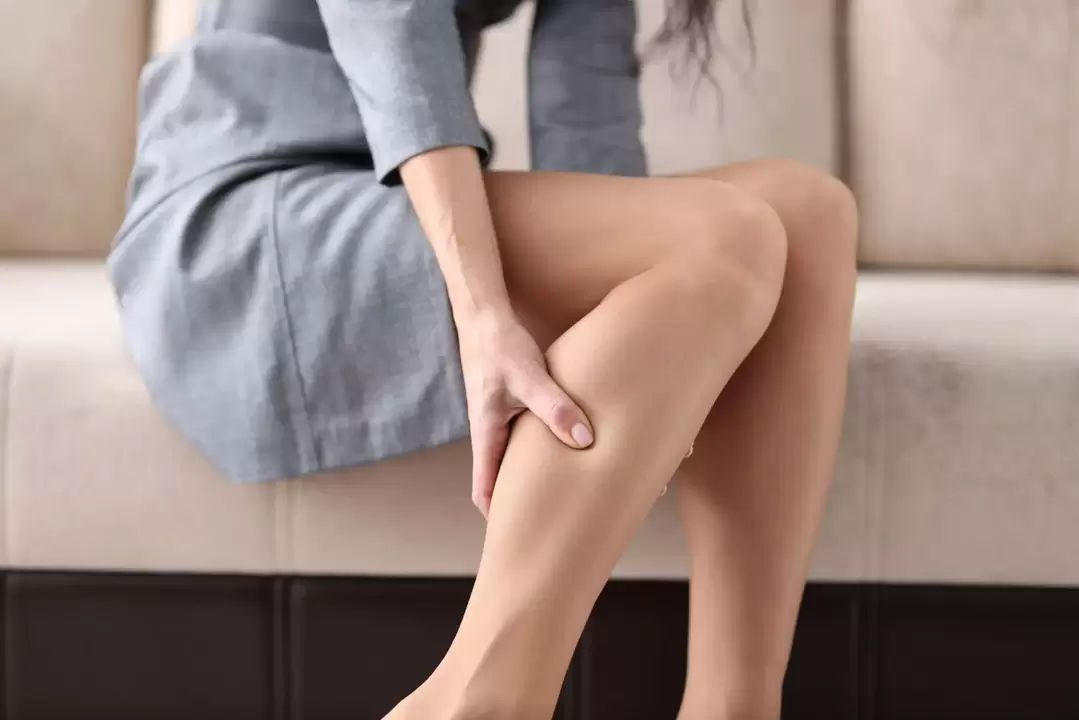
What do varicose veins look like?
Since varicose veins are a modification of veins, this disease is also referred to as a cosmetic problem:
- first, the patient notices the appearance of nets and patterns of veins in their legs;
- then the vein becomes tortuous, lifting the skin;
- in the most advanced stages, varicose nodes are clearly visible, representing the expansion and entanglement of blood vessels.
What is the danger of this disease?
What happens if the disease is not treated? It will definitely lead to complications. The most dangerous is thrombophlebitis and the "separation" of blood clots. 5% of all patients experience the same complication. With age, trophic ulcers often form, which are difficult to treat. The risk of complications from varicose veins increases over time.
Thrombophlebitis . As a result, blood clots form in the veins of the legs, which can break and block the arteries, leading to myocardial infarction.Venous thrombosis. Clogged vessels by blood clots. It is manifested by pain in the legs, which is aggravated by physical exertion.Pulmonary embolism . Obstruction of its lumen by a detached thrombus. Death can occur within the first half hour. If the clot is small, then a pulmonary infarction can occur.Trophic ulcer. Darkening and thinning of the skin with the appearance of further ulcers. Occurs as a result of tissue nutrient deficiency. Poor response to treatment.
Risk factors
Ancestry . If both parents have varicose veins, then for the child the probability of getting the disease is 90%, if one has 60%.Pregnancy. During this period, vein disease is provoked by 3 factors:- hormonal changes - the production of progesterone in large quantities relaxes the muscles, making the veins more vulnerable;
- the pressure of the uterus, which has increased in size - in connection with this, the outflow of blood from the legs worsens;
- an increase in blood volume by 20-30% - the leg venous valve cannot withstand the load, especially if it is initially weak;
Wrong diet. Uncontrolled consumption of processed foods, sugar and salt, fast food, fried and fatty foods, trans fats, preservatives and artificial additives from industrial products also leave their mark.Hormonal background. Hormonal activity can weaken the veins, which causes vasodilation and prevents the valves from closing normally.Tight clothes . Tightening belts, tight jeans and underwear disrupt the harmonious flow of blood, preventing blood circulation.High heels . When walking, the veins work with limits. This is due to the fact that the load is distributed unevenly - the main part falls on the front legs. Pain in the veins, swelling of the legs are early signs of varicose veins.
Diagnosis of varicose veins
In the early diagnosis of varicose veins, ultrasound technology is used - angioscanning and dopplerography.
Ultrasonic angioscanning (USAS) is an informative method for non-invasive examination of peripheral vessels. It makes it possible to obtain two-dimensional images of arteries, visualize intravascular structures, and evaluate the direction and properties of fluid flow.
In severe cases, when no response can be obtained with USAS, computed tomography (CT) is used.
Doppler ultrasound (Doppler ultrasound) is the easiest method to evaluate the peripheral vessels. He evaluates the state of the arteries with indirect indicators: blood flow response to functional tests, etc.
X-ray contrast phlebography is used in the diagnosis of arteriovenous angiodysplasia, acute thrombosis and its consequences, as well as small pelvic varicose veins.
Treatment of varicose veins
Surgical technique
Complete healing of varicose veins is possible only after surgical treatment. It is done in three ways:
- phlebectomy - removal of enlarged varicose vessels;
- sclerosing is the introduction of a special substance into the varicose veins, which "sticks together" the walls of the blood vessels, normalizing blood flow. Vein swelling disappears, even cosmetic defects disappear;
- laser coagulation - the vein wall is exposed to heat, as a result the vein lumen "closes". Manipulation is carried out only if the veins grow no more than 10 mm.
Medical treatment of varicose veins
The main role in the treatment is played by venotonics in the form of tablets. They improve the blood circulation process, heal the arteries.
Also prescribe venotonic drugs - phlebotonics. They are taken with thinning of blood vessel walls, increased permeability, reduced elasticity and fluid stagnation. The preparation strengthens the vein wall, increases its elasticity, reduces swelling and other negative signs. An additional quality of phlebotonics is the establishment of microcirculation in the affected area.
Antiplatelet agents are used to thin the blood in the veins. Medicines that are needed when you need to reduce the formation of blood clots. Indicated for patients with increased blood viscosity. You can take antiplatelet agents only if there is no tendency to bleeding.
Anticoagulants are sometimes used to stop thrombus formation individually. They eliminate blood clots, reduce viscosity. But the decision is made by the attending physician after evaluating the potential health benefits and potency of rice.
Compression therapy
A reliable helper in the treatment of varicose veins is a compression garment. The principle of operation of the product is as follows:
- when wearing compression stockings, the pressure on the superficial and deep veins increases;
- the greatest pressure is at the bottom, where the veins are narrower and the outflow of blood is the fastest;
- due to vein narrowing, valve operation improves;
- pain, swelling, fatigue in the legs disappeared.
A complex approach
There are many treatment options, but the most accurate is the emphasis on improving the whole organism as a whole. Varicose veins in the broadest sense are not only vein problems, but also symptoms that indicate damage in the body. Therefore, we advise you to keep your body healthy, and do it consistently and wisely.
- drink plenty of water - dehydration is one of the causes of blood clots, especially during hot periods;
- helps the liver in detoxification - add artichokes, hemp, grapefruit, oranges, apples, cruciferous vegetables, rosemary, dandelions, olives to the diet (make sure there are no allergic reactions and individual intolerance to the product);
- remove from the diet all pro-inflammatory foods that thicken blood and have a negative effect on the walls of blood vessels (alcohol, coffee, sugar, pastries, dairy products, smoked, canned food, fast food, refined food);
- eliminate constipation - they squeeze the pelvic venous blood flow. Start drinking symbionts or microbiotics. The bacteria in their composition create a balance of microflora and thus normalize the feces. They improve the condition of the small and large intestines, as well as the gastric mucosa;
- take an analysis for homocysteine - it should not exceed 10. If it is higher, you need to make sure that there is no deficiency of vitamin B12, folic acid and iron. At the same time, restore the microflora, otherwise its absorption may be affected;
- restore protein levels. For confirmation, a biochemical blood test is given: the optimal concentration of protein in adults should be 72-86 g / l, in children - 45 to 80 g / l. ;
- working with insulin resistance - often the problem goes hand in hand with this disorder. You can recognize by the symptoms: constant hunger and frequent desire to eat, various papillomas, red dots that look like moles, swelling, thirst and high blood pressure;
- introduce exercises - Pilates, yoga, light cardio;
- increase lymphatic outflow - drink water with herbs, cranberries, spices, lemon, ginger;
- contrast bath - under the influence of cold, small vessels begin to narrow, and under the influence of heat, on the contrary, expand. This leads to the strengthening of the vascular walls and an increase in their tone.
- restore hormone levels - excessive hormone production activity dilates blood vessels and prevents valves from closing normally. To support the process of restoring hormonal balance, the symbiont with broccoli is ideal. The active ingredient - sulforaphane - contained in it, removes excess estrogen from the body. This is due to the anti-carcinogenic content in broccoli, such as potassium, zinc, selenium, beta-carotene, amino acids, vitamins A, C and E.